Sucker Rod Chemical, Grade and Strength Chart
The sucker rod is utilized in the oil and gas industry to connect the surface and downhole compositions of an interchanging piston pump mounted in an oil well.
It is usually made of steel with threaded ends and measures from 25 to 30 feet long. A series of interconnected sucker rods connect the downhole pump deep down the well to the visible pumpjack above the ground that serves as drive for the well pump.
Fiberglass sucker rods, with a metallic female thread at one end and a male thread on the other, are also available in lengths of 37 ½ feet, as well as in three-fourth- seven-eighth, one, and one-and-one-fourth- inch diameters. Aside from steel and fiberglass, sucker rod chemical, grade, and strength may vary depending on the other types:
- Pony rod
- Low alloy rod
- Continuous solid rod
- Fiber reinforced plastic sucker rod
Sucker Rod Benefits
The sucker rod is an essential part of the sucker rod pump system that plays as a basic artificial lift structure. Sucker rods, along with other parts such as the beam, crank, and other compositions, are used together to deliver a mechanical reciprocating movement. Fluids are lifted up using the sucker rod string through the mechanical motion.
Sucker Rod Chemical, Grade, and Strength Chart
The Sucker Rod Chemical, Grade, and Strength Chart specifications are established through the API Spec. 11B, which presents the three primary grades of steels rods:
- Sucker Rod Grade C has the minimum and maximum tensile strengths ranging from 90,000 to 115,000 psi.
- Sucker Rod Grade K has a minimum tensile strength of 90,000 psi and a maximum of 115,000 psi. The chemical component of sucker rods in this category is 1.65 to 2.00% nickel, making them costlier than the sucker rod grade C but with better corrosion-associated properties.
- Sucker Rod Grade D comes with a minimum tensile strength of 115, 000 psi and a maximum of 140, 000 psi. This comes in three types, as specified by Spec. 11B: alloy, special-alloy steels, and plain carbon.
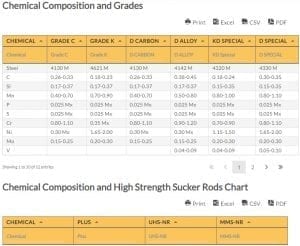
Chemical Composition and Grades
| Chemical | Grade C | Grade K | D CARBON | D ALLOY | KD Special | D SPECIAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | Chemical | Grade C | Grade K | D CARBON | D ALLOY | KD Special | D SPECIAL |
| 1 | Steel | 4130 M | 4621 M | 4130 M | 4142 M | 4320 M | 4330 M |
| 2 | C | 0.26-0.33 | 0.18-0.23 | 0.26-0.33 | 0.38-0.45 | 0.18-0.24 | 0.30-0.35 |
| 3 | Si | 0.17-0.37 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.15-0.35 |
| 4 | Mn | 0.40-0.70 | 0.70-0.90 | 0.40-0.70 | 0.50-0.80 | 0.80-1.00 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 5 | P | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 6 | S | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 7 | Cr | 0.80-1.10 | 0.35 Mx | 0.80-1.10 | 0.90-1.20 | 0.70-0.90 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 8 | Ni | 0.30 Mx | 1.65-2.00 | 0.30 Mx | 0.30 Mx | 1.15-1.50 | 1.65-2.00 |
| 9 | Mo | 0.15-0.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.20-0.30 |
| 10 | V | 0.04-0.09 | 0.04-0.09 | 0.05-0.10 |
Chemical Composition and Grades
| Chemical | Grade C | Grade K | D CARBON | D ALLOY | KD Special | D SPECIAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | Chemical | Grade C | Grade K | D CARBON | D ALLOY | KD Special | D SPECIAL |
| 1 | Steel | 4130 M | 4621 M | 4130 M | 4142 M | 4320 M | 4330 M |
| 2 | C | 0.26-0.33 | 0.18-0.23 | 0.26-0.33 | 0.38-0.45 | 0.18-0.24 | 0.30-0.35 |
| 3 | Si | 0.17-0.37 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.15-0.35 |
| 4 | Mn | 0.40-0.70 | 0.70-0.90 | 0.40-0.70 | 0.50-0.80 | 0.80-1.00 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 5 | P | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 6 | S | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 7 | Cr | 0.80-1.10 | 0.35 Mx | 0.80-1.10 | 0.90-1.20 | 0.70-0.90 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 8 | Ni | 0.30 Mx | 1.65-2.00 | 0.30 Mx | 0.30 Mx | 1.15-1.50 | 1.65-2.00 |
| 9 | Mo | 0.15-0.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.20-0.30 |
| 10 | V | 0.04-0.09 | 0.04-0.09 | 0.05-0.10 |
Chemical Composition and High Strength Sucker Rods Chart
| Chemical | Plus | UHS-NR | MMS-NR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | Chemical | Plus | UHS-NR | MMS-NR |
| 1 | Steel | 4130 M | 4330 M | 4138 M |
| 2 | C | 0.26-0.33 | 0.30-0.35 | 0.37-0.45 |
| 3 | Si | 0.17-0.37 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.17-0.37 |
| 4 | Mn | 0.40-0.70 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.90-1.20 |
| 5 | P | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 6 | S | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 7 | Cr | 0.80-1.10 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.90-1.20 |
| 8 | Ni | 0.30 Mx | 1.65-2.00 | 0.30 Mx |
| 9 | Mo | 0.15-0.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.20-0.30 |
| 10 | V | 0.05-0.10 |
Chemical Composition and High Strength Sucker Rods Chart
| Chemical | Plus | UHS-NR | MMS-NR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | Chemical | Plus | UHS-NR | MMS-NR |
| 1 | Steel | 4130 M | 4330 M | 4138 M |
| 2 | C | 0.26-0.33 | 0.30-0.35 | 0.37-0.45 |
| 3 | Si | 0.17-0.37 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.17-0.37 |
| 4 | Mn | 0.40-0.70 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.90-1.20 |
| 5 | P | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 6 | S | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx | 0.025 Mx |
| 7 | Cr | 0.80-1.10 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.90-1.20 |
| 8 | Ni | 0.30 Mx | 1.65-2.00 | 0.30 Mx |
| 9 | Mo | 0.15-0.25 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.20-0.30 |
| 10 | V | 0.05-0.10 |
The sucker rod minimum yield strength was not specified by the API, as seen from the chart of sucker rod chemical, grade, and Strength; however, it is still needed in the computation of the rod string yield strength.
Thus, it is advised that in case the manufacturer is not identified, the following standards must be used: 60,000 psi minimum yield strength for Sucker Rod Grade C and K, and 100,000 psi for Sucker Rod Grade D. Oil and gas industry operators should know that in order to maintain good operations, the minimum yield strength must be met.
Go here if you are looking for the Drill Collar Weight and Bending Strength Chart.


