Tubing Grade and Connection Type Chart
Tubing grade and connection type are relevant guidelines that help the industry understand the concept and process of tubing.
Tubing grade is a grade that follows the international standards recommended by the American Petroleum Institute (API) for the purpose of manufacturing, designing, and installing gas and oil pipelines. Aside from this, tubing connections are widely used because of their serviceable and excellent performance.
Tubing Grade and Connection Type: Application
It is also important to know the functions of the various tubing connections and tubing grade. This way, you will know which type fits best in different settings.
As per API standards, there are three types of connection tubing:
- Integral-joint tubing – It has a 10-round form along with a joint strength that measures less compared to its minimum body yield.
- External-upset tubing and coupling – This is globally utilized, as it works efficiently with wells and is considered 100% excellent with joint connections. For sealing and lubrication enhancements, it requires the thread compound as mentioned by API RP 5A3.
- Non-upset tubing and coupling – This type offers great advantage, as the diameter is less which is perfect for small clearance. Sizes are available from 1.050 to 4.500.
API standards must be followed all the time. These guidelines are used by the industry:
- T-95 is typically used for sour services and has a higher quality compared to C90
- H40 has low yield strength and is not utilized for tubing sizes
- C-75 is the only tubing grade which is no longer used as it fails to meet API standards
Tubing Grade and Connection Type Benefits
With the kind of connection and tubing grade, the tubing process is superior compared to piping. Tubing can be installed and maintained effortlessly. It takes 12 minutes to install a one-inch tubing system, while a pipe system needs at least 48 minutes. As the process requires less time, the cost is also affected. This means the tubing system is cheaper.
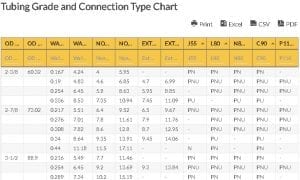
Tubing Grade and Connection Type Chart
| OD (in) | OD (mm) | Wall Thkns (in) | Wall Thkns (mm) | Non-Upset T&C lb/ft | Non-Upset T&C kg/m | Ext Upset T&C lb/ft | Ext Upset T&C kg/m | J55 | L80 | N80 | C90 | P110 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | OD (mm) | Wall Thkns (in) | Wall Thkns (mm) | Non-Upset T&C lb/ft | Non-Upset T&C kg/m | Ext Upset T&C lb/ft | Ext Upset T&C kg/m | J55 | L80 | N80 | C90 | P110 |
| 294 | 0.19 | 4.83 | 4.6 | 6.85 | 4.7 | 6.99 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 295 | 0.254 | 6.45 | 5.8 | 8.63 | 5.95 | 8.85 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 296 | 0.336 | 8.53 | 7.35 | 10.94 | 7.45 | 11.09 | PU | - | PU | PU | - | ||
| 297 | 2-7/8 | 73.02 | 0.217 | 5.51 | 6.4 | 9.52 | 6.5 | 9.67 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU |
| 298 | 0.276 | 7.01 | 7.8 | 11.61 | 7.9 | 11.76 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 299 | 0.308 | 7.82 | 8.6 | 12.8 | 8.7 | 12.95 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 300 | 0.34 | 8.64 | 9.35 | 13.91 | 9.45 | 14.06 | - | PU | - | PU | - | ||
| 301 | 0.44 | 11.18 | 11.5 | 17.11 | - | - | N | PN | - | PN | - | ||
| 302 | 3-1/2 | 88.9 | 0.216 | 5.49 | 7.7 | 11.46 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - |
| 303 | 0.254 | 6.45 | 9.2 | 13.69 | 9.3 | 13.84 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 304 | 0.289 | 7.34 | 10.2 | 15.19 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - | ||
| 305 | 0.375 | 9.52 | 12.7 | 18.91 | 12.95 | 19.27 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 306 | 4 | 101.6 | 0.226 | 5.74 | 9.5 | 14.14 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - |
| 307 | 0.262 | 6.65 | - | - | 11 | 16.37 | PU | PU | PU | PU | - | ||
| 308 | 4-1/2 | 114.3 | 0.271 | 6.88 | 12.6 | 18.75 | 12.75 | 18.97 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | - |
| 187 | 2-3/8 | 60.32 | 0.167 | 4.24 | 4 | 5.95 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - |
Tubing Grade and Connection Type Chart
| OD (in) | OD (mm) | Wall Thkns (in) | Wall Thkns (mm) | Non-Upset T&C lb/ft | Non-Upset T&C kg/m | Ext Upset T&C lb/ft | Ext Upset T&C kg/m | J55 | L80 | N80 | C90 | P110 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | OD (mm) | Wall Thkns (in) | Wall Thkns (mm) | Non-Upset T&C lb/ft | Non-Upset T&C kg/m | Ext Upset T&C lb/ft | Ext Upset T&C kg/m | J55 | L80 | N80 | C90 | P110 |
| 294 | 0.19 | 4.83 | 4.6 | 6.85 | 4.7 | 6.99 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 295 | 0.254 | 6.45 | 5.8 | 8.63 | 5.95 | 8.85 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 296 | 0.336 | 8.53 | 7.35 | 10.94 | 7.45 | 11.09 | PU | - | PU | PU | - | ||
| 297 | 2-7/8 | 73.02 | 0.217 | 5.51 | 6.4 | 9.52 | 6.5 | 9.67 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU |
| 298 | 0.276 | 7.01 | 7.8 | 11.61 | 7.9 | 11.76 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 299 | 0.308 | 7.82 | 8.6 | 12.8 | 8.7 | 12.95 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 300 | 0.34 | 8.64 | 9.35 | 13.91 | 9.45 | 14.06 | - | PU | - | PU | - | ||
| 301 | 0.44 | 11.18 | 11.5 | 17.11 | - | - | N | PN | - | PN | - | ||
| 302 | 3-1/2 | 88.9 | 0.216 | 5.49 | 7.7 | 11.46 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - |
| 303 | 0.254 | 6.45 | 9.2 | 13.69 | 9.3 | 13.84 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 304 | 0.289 | 7.34 | 10.2 | 15.19 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - | ||
| 305 | 0.375 | 9.52 | 12.7 | 18.91 | 12.95 | 19.27 | - | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | ||
| 306 | 4 | 101.6 | 0.226 | 5.74 | 9.5 | 14.14 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - |
| 307 | 0.262 | 6.65 | - | - | 11 | 16.37 | PU | PU | PU | PU | - | ||
| 308 | 4-1/2 | 114.3 | 0.271 | 6.88 | 12.6 | 18.75 | 12.75 | 18.97 | PNU | PNU | PNU | PNU | - |
| 187 | 2-3/8 | 60.32 | 0.167 | 4.24 | 4 | 5.95 | - | - | PN | PN | PN | PN | - |
Tubing Grade and Connection Type Chart Abbreviations:
- T & C – Threaded and Coupled Ends
- in – Inches
- mm -millimeter
- lb/ft – pounds per feet
- kg/m – kilogram per meter
- OD – Outer Diameter
- Wall Thkns – Wall Thickness
Metrication of Dimensions and Weight
- O.D X 25.4 = mm
- I.D x 25.4 = mm Wall x 25.4 = mm
- Lbs./ft. x 1.488 = kg/meter
Grade Types
- J-55 is more effective in wells with low and shallow pressure
- L-80 has various kinds such as 13 CR, 1 and 9 CR
- N80 is commonly utilized in gas and sweet oil wells
- C90 is a recently developed grade with two types
- P110 works for deep wells but are inefficient for sour condensate wells
Go here if you are looking for the Tubing Size and Grade Chart.


