Tubing Size and Grade Chart
Tubing Importance
The oil and gas industry is a complex and capital intensive venture. It is also time consuming and involves multi-processes from drilling to casing and tubing.
Tubing proceeds to vertical drilling of a wellhole using a drill bit. This reaches the oil deposits deep under the ground. Tubing also follows casing where the wellhole is cemented in place. Once the casing is stabilized, tubing brings or transports gas or oil either vertically or horizontally from deep in the well to the surface. A little similar to casing, with 4.5 inches in diameter being the threshold, tubing is inserted into the production casing to complete the process.
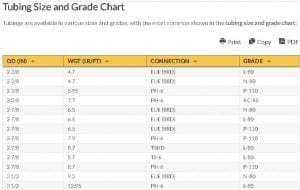
Tubing Size and Grade Chart
Tubings are available in various sizes and grades, with the most common shown in the tubing size and grade chart:
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | Wgt (lb/ft) | Connection | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 3/8 | 4.7 | EUE (8RD) | L-80 |
| 2 | 2 3/8 | 4.7 | EUE (8RD) | N-80 |
| 3 | 2 3/8 | 5.95 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 4 | 2 3/8 | 7.7 | PH-6 | AC-95 |
| 5 | 2 7/8 | 6.5 | EUE (8RD) | N-80 |
| 6 | 2 7/8 | 6.5 | EUE (8RD) | L-80 |
| 7 | 2 7/8 | 6.5 | EUE (8RD) | P-110 |
| 8 | 2 7/8 | 7.9 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 9 | 2 7/8 | 8.7 | TSHD | L-80 |
| 10 | 2 7/8 | 8.7 | TS-6 | L-80 |
| 11 | 2 7/8 | 8.7 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 12 | 3 1/2 | 9.3 | EUE (8RD) | N-80 |
| 13 | 3 1/2 | 12.95 | PH-6 | L-80 |
| 14 | 3 1/2 | 12.95 | BTS-6 | L-80 |
| 15 | 3 1/2 | 12.95 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 16 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | PH-6 | AC-95 |
| 17 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | BTS-6 | T-95 |
| 18 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | PH-6 | T-95 |
| 19 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | TS-6 | C-95SS |
| 20 | 4 1/2 | 11.6 | LTC 8RD | P-110 |
| 21 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | BTS-6 | L-80 |
| 22 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | PH-6 | AC-95 |
| 23 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | TS-6 | C-95SS |
| 24 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 25 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | BTS-6 | P-110 |
| 26 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | TS-6 | P-110 |
| 27 | 4 1/2 | 17 | TSHD | Q-125 |
| 28 | 4 1/2 | 24 | PH-4 | C-95 |
| 29 | 4 1/2 | 24 | PH-4 | NT-95SS |
| 30 | 5 | 23.2 | HYDRIL CS | AC-95 |
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | Wgt (lb/ft) | Connection | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 3/8 | 4.7 | EUE (8RD) | L-80 |
| 2 | 2 3/8 | 4.7 | EUE (8RD) | N-80 |
| 3 | 2 3/8 | 5.95 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 4 | 2 3/8 | 7.7 | PH-6 | AC-95 |
| 5 | 2 7/8 | 6.5 | EUE (8RD) | N-80 |
| 6 | 2 7/8 | 6.5 | EUE (8RD) | L-80 |
| 7 | 2 7/8 | 6.5 | EUE (8RD) | P-110 |
| 8 | 2 7/8 | 7.9 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 9 | 2 7/8 | 8.7 | TSHD | L-80 |
| 10 | 2 7/8 | 8.7 | TS-6 | L-80 |
| 11 | 2 7/8 | 8.7 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 12 | 3 1/2 | 9.3 | EUE (8RD) | N-80 |
| 13 | 3 1/2 | 12.95 | PH-6 | L-80 |
| 14 | 3 1/2 | 12.95 | BTS-6 | L-80 |
| 15 | 3 1/2 | 12.95 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 16 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | PH-6 | AC-95 |
| 17 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | BTS-6 | T-95 |
| 18 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | PH-6 | T-95 |
| 19 | 3 1/2 | 15.8 | TS-6 | C-95SS |
| 20 | 4 1/2 | 11.6 | LTC 8RD | P-110 |
| 21 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | BTS-6 | L-80 |
| 22 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | PH-6 | AC-95 |
| 23 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | TS-6 | C-95SS |
| 24 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | PH-6 | P-110 |
| 25 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | BTS-6 | P-110 |
| 26 | 4 1/2 | 15.5 | TS-6 | P-110 |
| 27 | 4 1/2 | 17 | TSHD | Q-125 |
| 28 | 4 1/2 | 24 | PH-4 | C-95 |
| 29 | 4 1/2 | 24 | PH-4 | NT-95SS |
| 30 | 5 | 23.2 | HYDRIL CS | AC-95 |
For tubing, the most important dimensions are its outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness (WT), as these measurements express the true dimensional value of this hollow metal. OD’s precise measure will indicate the maximum weight the tubing can withstand. Both OD and WT are expressed in inches or millimeters. Other key measurements consist of mechanical properties like tensile strength, yield, and elongation.
Tubing Size and Grade Chart Abbreviations:
- in – inches
- lb/ft – pounds per feet
- EUE – External Upset End
- TSHD – Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger
- LT – Linear Time
- OD – Outer Diameter
- WGT – Weight
Tubing Types
Tubing can be customized to specific operating conditions. Commonly used tubing types include the following:
- H-40 type is an economical option designed for shallow wells.
- J-55 is the most common tubing used for medium depth wells which can be up to 7,000 ft deep.
- C-75 is the improved version of J-55; It is used in wells with similar depths, but is not common.
- N-80 is a pipe designed for 12,000 ft or more in depth wells.
- P-105 is a heavy duty pipe intended for use in high-gas pressure formations or for deep wells.
Tubing Options
Tubing is basically a seamless pipe, sold at irregular lengths ranging from 28 to 40 ft. A tubing string is put together by selecting and putting together an appropriate mix of lengths of tubing joints. Joints are available from 2 to 12 ft long with a 2 ft step increment for each size.
Tubings are made with different wall thickness and several metal quality: mild steel, stainless steel, brass, copper, chrome, and aluminum which affect the costs. These make them costlier than pipe.
Tubing Specifications
Tubes are manufactured under strict specifications and must be tested for tensile strength and hardness. Steel tubings used in high pressure condition come in short OD (up to 5 inches), while tubulars that are used for mechanical application are available in higher length diameters.
Go here if you are looking for the Tubing Grade and Connection Type Chart.


