Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Chart
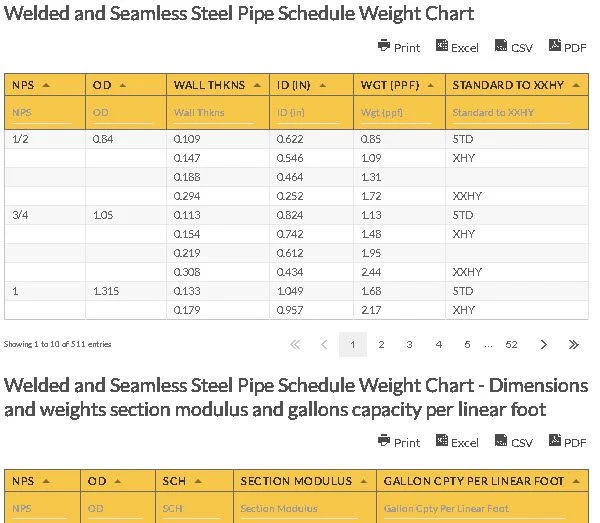
The Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Chart provides an overview of the two main pipes used in the oil and gas industry. The table also provides specific information on how efficient the pipe is. Details include the accurate gallon capacity per linear foot. It also supplies data on pipe schedule or wall thickness.
Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Discussion
The line pipe manufacturing industry produces two types of pipe: welded steel pipe and seamless steel pipe. They have significant differences in terms of production cost and steel grade.
Welded steel pipe is used widely in automobiles, boilers, furniture, scaffolding, and other industries. This steel pipe is a tubular material that is made from flat plates, known as skelp that is formed to prepare for welding. To ensure high-quality standards, a radiological or ultrasonic inspection is performed together with a pressure test. Listed below are the benefits of using welded steel pipe:
- It is cost effective compared to seamless pipe
- Its wall thickness is consistent
- It is possible to inspect the internal surface before manufacturing
Meanwhile, seamless line pipe is made from a cylindrical bar heated to a high temperature before piercing it to make a hole through the cylinder. The roller sizes are used to create the pipe’s wall thickness and correct diameter. The process creates small diameter pipe ranging from 0.5 to 24 inches.
Here are some benefits of using seamless line pipe:
- Pressure ratings are increased
- It has increased strength under heavy load
- It has uniform shape
Increased pressure rating is the seamless line pipe’s best benefit, as it has increased ability to resist heavy loads. While it is a bit expensive, lighter and thinner sizes can be an option to reduce the expenses.
Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Chart
| wdt_ID | NPS | OD | Wall Thkns | ID (in) | Wgt (ppf) | Std to XXHY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2 | 0.84 | 0.109 | 0.622 | 0.85 | STD |
| 2 | 0.147 | 0.546 | 1.09 | XHY | ||
| 3 | 0.188 | 0.464 | 1.31 | |||
| 4 | 0.294 | 0.252 | 1.72 | XXHY | ||
| 5 | 3/4 | 1.05 | 0.113 | 0.824 | 1.13 | STD |
| 6 | 0.154 | 0.742 | 1.48 | XHY | ||
| 7 | 0.219 | 0.612 | 1.95 | |||
| 8 | 0.308 | 0.434 | 2.44 | XXHY | ||
| 9 | 1 | 1.315 | 0.133 | 1.049 | 1.68 | STD |
| 10 | 0.179 | 0.957 | 2.17 | XHY | ||
| 11 | 0.25 | 0.815 | 2.85 | |||
| 12 | 0.358 | 0.599 | 3.66 | XXHY | ||
| 13 | 1 1/4 | 1.66 | 0.14 | 1.38 | 2.27 | STD |
| 14 | 0.191 | 1.278 | 3 | XHY | ||
| 15 | 0.25 | 1.16 | 3.77 | |||
| 16 | 0.382 | 0.896 | 5.22 | |||
| 17 | 1 1/2 | 1.9 | 0.145 | 1.61 | 2.72 | STD |
| 18 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 3.63 | XHY | ||
| 19 | 0.281 | 1.338 | 4.86 | |||
| 20 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 6.41 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 2.375 | 0.109 | 2.157 | 2.64 | |
| 22 | 0.154 | 2.067 | 3.66 | STD | ||
| 23 | 0.218 | 1.939 | 5.03 | XHY | ||
| 24 | 0.25 | 1.875 | 5.68 | |||
| 25 | 0.281 | 1.813 | 6.29 | |||
| 26 | 0.344 | 1.687 | 7.47 | |||
| 27 | 0.436 | 1.503 | 9.04 | XXHY | ||
| 28 | 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 0.12 | 2.635 | 3.53 | |
| 29 | 0.203 | 2.469 | 5.8 | STD. | ||
| 30 | 0.216 | 2.443 | 6.14 | |||
| 31 | 0.25 | 2.375 | 7.02 | |||
| 32 | 0.276 | 2.323 | 7.67 | XHY | ||
| 33 | 0.375 | 2.125 | 10.02 | |||
| 34 | 0.552 | 1.771 | 13.71 | XXXHY | ||
| 35 | 3 | 3.5 | 0.12 | 3.26 | 4.34 | |
| 36 | 0.156 | 3.188 | 5.58 | |||
| 37 | 0.172 | 3.156 | 6.12 | |||
| 38 | 0.188 | 3.124 | 6.66 | |||
| 39 | 0.216 | 3.068 | 7.58 | STD. | ||
| 40 | 0.25 | 3 | 8.69 | |||
| 41 | 0.281 | 2.938 | 9.67 | |||
| 42 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 10.26 | XHY | ||
| 43 | 0.438 | 2.624 | 14.34 | |||
| 44 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 18.6 | XXHY | ||
| 45 | 3 1/2 | 4 | 0.12 | 3.76 | 4.98 | |
| 46 | 0.226 | 3.548 | 9.12 | STD. | ||
| 47 | 0.25 | 3.5 | 10.02 | |||
| 48 | 0.281 | 3.438 | 11.17 | |||
| 49 | 0.318 | 3.364 | 12.52 | XHY | ||
| 50 | 0.636 | 2..728 | 22.87 | XXHY | ||
| 51 | 4 | 4.5 | 0.12 | 4.26 | 5.62 | |
| 52 | 0.156 | 4.188 | 7.24 | |||
| 53 | 0.188 | 4.124 | 8.67 | |||
| 54 | 0.203 | 4.094 | 9.32 | |||
| 55 | 0.219 | 4.062 | 10.02 | |||
| 56 | 0.237 | 4.026 | 10.8 | STD. | ||
| 57 | 0.25 | 4 | 11.36 | |||
| 58 | 0.281 | 3.938 | 12.67 | |||
| 59 | 0.312 | 3.876 | 13.97 | |||
| 60 | 0.337 | 3.826 | 15 | XHY | ||
| 61 | 0.438 | 3.624 | 19.02 | |||
| 62 | 0.531 | 3.438 | 22.53 | |||
| 63 | 0.674 | 3.152 | 27.57 | XXHY | ||
| 64 | 5 | 5.563 | 0.188 | 5.187 | 10.8 | |
| 65 | 0.219 | 5.125 | 12.51 | |||
| 66 | 0.258 | 5.047 | 14.63 | STD. | ||
| 67 | 0.281 | 5.001 | 15.87 | |||
| 68 | 0.312 | 4.939 | 17.51 | |||
| 69 | 0.344 | 4.875 | 19.19 | |||
| 70 | 0.375 | 4.813 | 20.8 | XHY | ||
| 71 | 0.5 | 4.563 | 27.06 | |||
| 72 | 0.625 | 4.313 | 32.99 | |||
| 73 | 0.75 | 4.063 | 38.59 | XXHY | ||
| 74 | 6 | 6.625 | 0.109 | 6.407 | 7.59 | |
| 75 | 0.134 | 6.357 | 9.3 | |||
| 76 | 0.156 | 6.313 | 10.79 | |||
| 77 | 0.188 | 6.249 | 12.94 | |||
| 78 | 0.203 | 6.219 | 13.94 | |||
| 79 | 0.219 | 6.187 | 15 | |||
| 80 | 0.25 | 6.125 | 17.04 | |||
| 81 | 0.28 | 6.065 | 18.99 | STD. | ||
| 82 | 0.312 | 6.001 | 21.06 | |||
| 83 | 0.344 | 5.937 | 23.1 | |||
| 84 | 0.375 | 5.875 | 25.05 | |||
| 85 | 0.432 | 5.761 | 28.6 | XHY | ||
| 86 | 0.5 | 5.625 | 32.74 | |||
| 87 | 0.562 | 5.501 | 36.43 | |||
| 88 | 0.625 | 5.375 | 40.09 | |||
| 89 | 0.719 | 5.187 | 45.39 | |||
| 90 | 0.864 | 4.897 | 53.21 | XXHY | ||
| 91 | 1 | 4.625 | 60.13 | |||
| 92 | 1.125 | 4.375 | 66.14 | |||
| 93 | 8 | 8.625 | 0.188 | 8.25 | 16.96 | |
| 94 | 0.203 | 8.219 | 18.28 | |||
| 95 | 0.219 | 8.187 | 19.68 | |||
| 96 | 0.237 | 8.151 | 21.25 | |||
| 97 | 0.25 | 8.125 | 22.38 | |||
| 98 | 0.277 | 8.071 | 24.72 | |||
| 99 | 0.312 | 8.001 | 27.73 | |||
| 100 | 0.322 | 7.981 | 28.58 | STD. |
| wdt_ID | NPS | OD | Wall Thkns | ID (in) | Wgt (ppf) | Std to XXHY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2 | 0.84 | 0.109 | 0.622 | 0.85 | STD |
| 2 | 0.147 | 0.546 | 1.09 | XHY | ||
| 3 | 0.188 | 0.464 | 1.31 | |||
| 4 | 0.294 | 0.252 | 1.72 | XXHY | ||
| 5 | 3/4 | 1.05 | 0.113 | 0.824 | 1.13 | STD |
| 6 | 0.154 | 0.742 | 1.48 | XHY | ||
| 7 | 0.219 | 0.612 | 1.95 | |||
| 8 | 0.308 | 0.434 | 2.44 | XXHY | ||
| 9 | 1 | 1.315 | 0.133 | 1.049 | 1.68 | STD |
| 10 | 0.179 | 0.957 | 2.17 | XHY | ||
| 11 | 0.25 | 0.815 | 2.85 | |||
| 12 | 0.358 | 0.599 | 3.66 | XXHY | ||
| 13 | 1 1/4 | 1.66 | 0.14 | 1.38 | 2.27 | STD |
| 14 | 0.191 | 1.278 | 3 | XHY | ||
| 15 | 0.25 | 1.16 | 3.77 | |||
| 16 | 0.382 | 0.896 | 5.22 | |||
| 17 | 1 1/2 | 1.9 | 0.145 | 1.61 | 2.72 | STD |
| 18 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 3.63 | XHY | ||
| 19 | 0.281 | 1.338 | 4.86 | |||
| 20 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 6.41 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 2.375 | 0.109 | 2.157 | 2.64 | |
| 22 | 0.154 | 2.067 | 3.66 | STD | ||
| 23 | 0.218 | 1.939 | 5.03 | XHY | ||
| 24 | 0.25 | 1.875 | 5.68 | |||
| 25 | 0.281 | 1.813 | 6.29 | |||
| 26 | 0.344 | 1.687 | 7.47 | |||
| 27 | 0.436 | 1.503 | 9.04 | XXHY | ||
| 28 | 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 0.12 | 2.635 | 3.53 | |
| 29 | 0.203 | 2.469 | 5.8 | STD. | ||
| 30 | 0.216 | 2.443 | 6.14 | |||
| 31 | 0.25 | 2.375 | 7.02 | |||
| 32 | 0.276 | 2.323 | 7.67 | XHY | ||
| 33 | 0.375 | 2.125 | 10.02 | |||
| 34 | 0.552 | 1.771 | 13.71 | XXXHY | ||
| 35 | 3 | 3.5 | 0.12 | 3.26 | 4.34 | |
| 36 | 0.156 | 3.188 | 5.58 | |||
| 37 | 0.172 | 3.156 | 6.12 | |||
| 38 | 0.188 | 3.124 | 6.66 | |||
| 39 | 0.216 | 3.068 | 7.58 | STD. | ||
| 40 | 0.25 | 3 | 8.69 | |||
| 41 | 0.281 | 2.938 | 9.67 | |||
| 42 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 10.26 | XHY | ||
| 43 | 0.438 | 2.624 | 14.34 | |||
| 44 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 18.6 | XXHY | ||
| 45 | 3 1/2 | 4 | 0.12 | 3.76 | 4.98 | |
| 46 | 0.226 | 3.548 | 9.12 | STD. | ||
| 47 | 0.25 | 3.5 | 10.02 | |||
| 48 | 0.281 | 3.438 | 11.17 | |||
| 49 | 0.318 | 3.364 | 12.52 | XHY | ||
| 50 | 0.636 | 2..728 | 22.87 | XXHY | ||
| 51 | 4 | 4.5 | 0.12 | 4.26 | 5.62 | |
| 52 | 0.156 | 4.188 | 7.24 | |||
| 53 | 0.188 | 4.124 | 8.67 | |||
| 54 | 0.203 | 4.094 | 9.32 | |||
| 55 | 0.219 | 4.062 | 10.02 | |||
| 56 | 0.237 | 4.026 | 10.8 | STD. | ||
| 57 | 0.25 | 4 | 11.36 | |||
| 58 | 0.281 | 3.938 | 12.67 | |||
| 59 | 0.312 | 3.876 | 13.97 | |||
| 60 | 0.337 | 3.826 | 15 | XHY | ||
| 61 | 0.438 | 3.624 | 19.02 | |||
| 62 | 0.531 | 3.438 | 22.53 | |||
| 63 | 0.674 | 3.152 | 27.57 | XXHY | ||
| 64 | 5 | 5.563 | 0.188 | 5.187 | 10.8 | |
| 65 | 0.219 | 5.125 | 12.51 | |||
| 66 | 0.258 | 5.047 | 14.63 | STD. | ||
| 67 | 0.281 | 5.001 | 15.87 | |||
| 68 | 0.312 | 4.939 | 17.51 | |||
| 69 | 0.344 | 4.875 | 19.19 | |||
| 70 | 0.375 | 4.813 | 20.8 | XHY | ||
| 71 | 0.5 | 4.563 | 27.06 | |||
| 72 | 0.625 | 4.313 | 32.99 | |||
| 73 | 0.75 | 4.063 | 38.59 | XXHY | ||
| 74 | 6 | 6.625 | 0.109 | 6.407 | 7.59 | |
| 75 | 0.134 | 6.357 | 9.3 | |||
| 76 | 0.156 | 6.313 | 10.79 | |||
| 77 | 0.188 | 6.249 | 12.94 | |||
| 78 | 0.203 | 6.219 | 13.94 | |||
| 79 | 0.219 | 6.187 | 15 | |||
| 80 | 0.25 | 6.125 | 17.04 | |||
| 81 | 0.28 | 6.065 | 18.99 | STD. | ||
| 82 | 0.312 | 6.001 | 21.06 | |||
| 83 | 0.344 | 5.937 | 23.1 | |||
| 84 | 0.375 | 5.875 | 25.05 | |||
| 85 | 0.432 | 5.761 | 28.6 | XHY | ||
| 86 | 0.5 | 5.625 | 32.74 | |||
| 87 | 0.562 | 5.501 | 36.43 | |||
| 88 | 0.625 | 5.375 | 40.09 | |||
| 89 | 0.719 | 5.187 | 45.39 | |||
| 90 | 0.864 | 4.897 | 53.21 | XXHY | ||
| 91 | 1 | 4.625 | 60.13 | |||
| 92 | 1.125 | 4.375 | 66.14 | |||
| 93 | 8 | 8.625 | 0.188 | 8.25 | 16.96 | |
| 94 | 0.203 | 8.219 | 18.28 | |||
| 95 | 0.219 | 8.187 | 19.68 | |||
| 96 | 0.237 | 8.151 | 21.25 | |||
| 97 | 0.25 | 8.125 | 22.38 | |||
| 98 | 0.277 | 8.071 | 24.72 | |||
| 99 | 0.312 | 8.001 | 27.73 | |||
| 100 | 0.322 | 7.981 | 28.58 | STD. |
Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Chart – Dimensions and weights section modulus and gallons capacity per linear foot
| wdt_ID | NPS | OD | SCH | Section Modulus | Gallon Cpty Per Linear Foot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2 | 0.84 | 40 | 0.0407 | 0.0158 |
| 2 | 80 | 0.0478 | 0.0122 | ||
| 3 | 160 | 0.0528 | 0.0088 | ||
| 4 | 0.0577 | 0.0026 | |||
| 5 | 3/4 | 1.05 | 40 | 0.0705 | 0.0277 |
| 6 | 80 | 0.0853 | 0.0225 | ||
| 7 | 160 | 0.1006 | 0.0153 | ||
| 8 | 0.1103 | 0.0077 | |||
| 9 | 1 | 1.315 | 40 | 0.1328 | 0.0449 |
| 10 | 80 | 0.1606 | 0.0374 | ||
| 11 | 160 | 0.1904 | 0.0271 | ||
| 12 | 0.2136 | 0.0146 | |||
| 13 | 1 1/4 | 1.66 | 40 | 0.2346 | 0.0777 |
| 14 | 80 | 0.2913 | 0.0666 | ||
| 15 | 160 | 0.3421 | 0.0549 | ||
| 16 | 0.411 | 0.0328 | |||
| 17 | 1 1/2 | 1.9 | 40 | 0.3262 | 0.1058 |
| 18 | 80 | 0.4118 | 0.0918 | ||
| 19 | 160 | 0.5079 | 0.073 | ||
| 20 | 0.5977 | 0.0494 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 2.375 | 10 | 0.4205 | 0.1898 |
| 22 | 40 | 0.5606 | 0.1743 | ||
| 23 | 80 | 0.7309 | 0.1534 | ||
| 24 | 0.8045 | 0.1434 | |||
| 25 | 0.8666 | 0.1344 | |||
| 26 | 160 | 0.9806 | 0.1161 | ||
| 27 | 1.1043 | 0.0922 | |||
| 28 | 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 10 | 0.687 | 0.2833 |
| 29 | 40 | 1.064 | 0.2487 | ||
| 30 | 1.1169 | 0.2435 | |||
| 31 | 1.2468 | 0.2301 | |||
| 32 | 80 | 1.3386 | 0.2202 | ||
| 33 | 160 | 1.6371 | 0.1842 | ||
| 34 | 1.9971 | 0.128 | |||
| 35 | 3 | 3.5 | 1.0411 | 0.4336 | |
| 36 | 1.3122 | 0.4147 | |||
| 37 | 1.4265 | 0.4064 | |||
| 38 | 1.5342 | 0.3984 | |||
| 39 | 40 | 1.7241 | 0.384 | ||
| 40 | 1.9372 | 0.3672 | |||
| 41 | 2.1207 | 0.3521 | |||
| 42 | 80 | 2.2253 | 0.3431 | ||
| 43 | 160 | 2.8774 | 0.2811 | ||
| 44 | 3.4243 | 0.2158 | |||
| 45 | 3 1/2 | 4 | 10 | 1.3776 | 0.5768 |
| 46 | 140 | 2.3939 | 0.5136 | ||
| 47 | 2.6001 | 0.4998 | |||
| 48 | 2.8562 | 0.4821 | |||
| 49 | 80 | 3.14 | 0.4617 | ||
| 50 | 4.8795 | 0.3085 | |||
| 51 | 4 | 4.5 | 10 | 1.7612 | 0.7404 |
| 52 | 2.2354 | 0.7156 | |||
| 53 | 2.6296 | 0.6942 | |||
| 54 | 2.8173 | 0.6838 | |||
| 55 | 3.0184 | 0.6725 | |||
| 56 | 40 | 3.2145 | 0.6613 | ||
| 57 | 3.3611 | 0.6528 | |||
| 58 | 60 | 3.7021 | 0.6326 | ||
| 59 | 4.0273 | 0.6126 | |||
| 60 | 80 | 4.2713 | 0.5972 | ||
| 61 | 120 | 5.179 | 0.5361 | ||
| 62 | 160 | 5.8997 | 0.4822 | ||
| 63 | 6.7927 | 0.4054 | |||
| 64 | 5 | 5.563 | 4.1161 | 1.0979 | |
| 65 | 4.7279 | 1.0716 | |||
| 66 | 40 | 5.45 | 1.0391 | ||
| 67 | 5.8644 | 1.0204 | |||
| 68 | 6.4074 | 0.99647 | |||
| 69 | 6.9358 | 0.9696 | |||
| 70 | 80 | 7.43 | 0.9449 | ||
| 71 | 120 | 9.2534 | 0.8495 | ||
| 72 | 160 | 10.7976 | 0.759 | ||
| 73 | 12.0954 | 0.6734 | |||
| 74 | 6 | 6.625 | 5 | 3.5769 | 1.6748 |
| 75 | 10 | 4.3475 | 1.6488 | ||
| 76 | 5.0107 | 1.626 | |||
| 77 | 5.9351 | 1.5937 | |||
| 78 | 6.3804 | 1.578 | |||
| 79 | 6.8261 | 1.562 | |||
| 80 | 7.6905 | 1.5306 | |||
| 81 | 40 | 8.4958 | 1.5008 | ||
| 82 | 9.3416 | 1.4688 | |||
| 83 | 10.111 | 1.4391 | |||
| 84 | 10.893 | 1.4082 | |||
| 85 | 80 | 12.224 | 1.3541 | ||
| 86 | 13.711 | 1.2909 | |||
| 87 | 120 | 14.9806 | 1.2346 | ||
| 88 | 16.1821 | 1.1787 | |||
| 89 | 160 | 17.8243 | 1.0977 | ||
| 90 | 20.025 | 0.9784 | |||
| 91 | 21.7719 | 0.8727 | |||
| 92 | 23.1237 | 0.7809 | |||
| 93 | 8 | 8.625 | 10.287 | 2.7769 | |
| 94 | 11.049 | 2.7561 | |||
| 95 | 11.841 | 2.735 | |||
| 96 | 12.796 | 2.7094 | |||
| 97 | 20 | 13.385 | 2.6934 | ||
| 98 | 30 | 14.69 | 2.6577 | ||
| 99 | 16.368 | 2.6112 | |||
| 100 | 40 | 16.809 | 2.5988 |
| wdt_ID | NPS | OD | SCH | Section Modulus | Gallon Cpty Per Linear Foot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2 | 0.84 | 40 | 0.0407 | 0.0158 |
| 2 | 80 | 0.0478 | 0.0122 | ||
| 3 | 160 | 0.0528 | 0.0088 | ||
| 4 | 0.0577 | 0.0026 | |||
| 5 | 3/4 | 1.05 | 40 | 0.0705 | 0.0277 |
| 6 | 80 | 0.0853 | 0.0225 | ||
| 7 | 160 | 0.1006 | 0.0153 | ||
| 8 | 0.1103 | 0.0077 | |||
| 9 | 1 | 1.315 | 40 | 0.1328 | 0.0449 |
| 10 | 80 | 0.1606 | 0.0374 | ||
| 11 | 160 | 0.1904 | 0.0271 | ||
| 12 | 0.2136 | 0.0146 | |||
| 13 | 1 1/4 | 1.66 | 40 | 0.2346 | 0.0777 |
| 14 | 80 | 0.2913 | 0.0666 | ||
| 15 | 160 | 0.3421 | 0.0549 | ||
| 16 | 0.411 | 0.0328 | |||
| 17 | 1 1/2 | 1.9 | 40 | 0.3262 | 0.1058 |
| 18 | 80 | 0.4118 | 0.0918 | ||
| 19 | 160 | 0.5079 | 0.073 | ||
| 20 | 0.5977 | 0.0494 | |||
| 21 | 2 | 2.375 | 10 | 0.4205 | 0.1898 |
| 22 | 40 | 0.5606 | 0.1743 | ||
| 23 | 80 | 0.7309 | 0.1534 | ||
| 24 | 0.8045 | 0.1434 | |||
| 25 | 0.8666 | 0.1344 | |||
| 26 | 160 | 0.9806 | 0.1161 | ||
| 27 | 1.1043 | 0.0922 | |||
| 28 | 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 10 | 0.687 | 0.2833 |
| 29 | 40 | 1.064 | 0.2487 | ||
| 30 | 1.1169 | 0.2435 | |||
| 31 | 1.2468 | 0.2301 | |||
| 32 | 80 | 1.3386 | 0.2202 | ||
| 33 | 160 | 1.6371 | 0.1842 | ||
| 34 | 1.9971 | 0.128 | |||
| 35 | 3 | 3.5 | 1.0411 | 0.4336 | |
| 36 | 1.3122 | 0.4147 | |||
| 37 | 1.4265 | 0.4064 | |||
| 38 | 1.5342 | 0.3984 | |||
| 39 | 40 | 1.7241 | 0.384 | ||
| 40 | 1.9372 | 0.3672 | |||
| 41 | 2.1207 | 0.3521 | |||
| 42 | 80 | 2.2253 | 0.3431 | ||
| 43 | 160 | 2.8774 | 0.2811 | ||
| 44 | 3.4243 | 0.2158 | |||
| 45 | 3 1/2 | 4 | 10 | 1.3776 | 0.5768 |
| 46 | 140 | 2.3939 | 0.5136 | ||
| 47 | 2.6001 | 0.4998 | |||
| 48 | 2.8562 | 0.4821 | |||
| 49 | 80 | 3.14 | 0.4617 | ||
| 50 | 4.8795 | 0.3085 | |||
| 51 | 4 | 4.5 | 10 | 1.7612 | 0.7404 |
| 52 | 2.2354 | 0.7156 | |||
| 53 | 2.6296 | 0.6942 | |||
| 54 | 2.8173 | 0.6838 | |||
| 55 | 3.0184 | 0.6725 | |||
| 56 | 40 | 3.2145 | 0.6613 | ||
| 57 | 3.3611 | 0.6528 | |||
| 58 | 60 | 3.7021 | 0.6326 | ||
| 59 | 4.0273 | 0.6126 | |||
| 60 | 80 | 4.2713 | 0.5972 | ||
| 61 | 120 | 5.179 | 0.5361 | ||
| 62 | 160 | 5.8997 | 0.4822 | ||
| 63 | 6.7927 | 0.4054 | |||
| 64 | 5 | 5.563 | 4.1161 | 1.0979 | |
| 65 | 4.7279 | 1.0716 | |||
| 66 | 40 | 5.45 | 1.0391 | ||
| 67 | 5.8644 | 1.0204 | |||
| 68 | 6.4074 | 0.99647 | |||
| 69 | 6.9358 | 0.9696 | |||
| 70 | 80 | 7.43 | 0.9449 | ||
| 71 | 120 | 9.2534 | 0.8495 | ||
| 72 | 160 | 10.7976 | 0.759 | ||
| 73 | 12.0954 | 0.6734 | |||
| 74 | 6 | 6.625 | 5 | 3.5769 | 1.6748 |
| 75 | 10 | 4.3475 | 1.6488 | ||
| 76 | 5.0107 | 1.626 | |||
| 77 | 5.9351 | 1.5937 | |||
| 78 | 6.3804 | 1.578 | |||
| 79 | 6.8261 | 1.562 | |||
| 80 | 7.6905 | 1.5306 | |||
| 81 | 40 | 8.4958 | 1.5008 | ||
| 82 | 9.3416 | 1.4688 | |||
| 83 | 10.111 | 1.4391 | |||
| 84 | 10.893 | 1.4082 | |||
| 85 | 80 | 12.224 | 1.3541 | ||
| 86 | 13.711 | 1.2909 | |||
| 87 | 120 | 14.9806 | 1.2346 | ||
| 88 | 16.1821 | 1.1787 | |||
| 89 | 160 | 17.8243 | 1.0977 | ||
| 90 | 20.025 | 0.9784 | |||
| 91 | 21.7719 | 0.8727 | |||
| 92 | 23.1237 | 0.7809 | |||
| 93 | 8 | 8.625 | 10.287 | 2.7769 | |
| 94 | 11.049 | 2.7561 | |||
| 95 | 11.841 | 2.735 | |||
| 96 | 12.796 | 2.7094 | |||
| 97 | 20 | 13.385 | 2.6934 | ||
| 98 | 30 | 14.69 | 2.6577 | ||
| 99 | 16.368 | 2.6112 | |||
| 100 | 40 | 16.809 | 2.5988 |
Terms Used:
Nominal pipe size is an international standard used to determine the diameter of a certain pipe.
Pipe schedule defines a pipe’s wall thickness. Examples include SCH: 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, and 160.
- O.D= Outside diameter
- I.D = Inside diameter
- wall = Wall thickness
- lbs/ft = lbs/ft
- STD= Standard weight.
Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Chart Abbreviations:
- O.D. – Outer Diameter
- I.D. – Inner Diameter
- STD – Standard
- SCH – Schedule
- XHY – Extra Heavy
- XXHY – Double Extra Heavy
- NPS – Nominal Pipe Size
Pipe Size Formula:
- O.D X 25.4 = mm
- I.D x 25.4 = mm Wall x 25.4 = mm
- Lbs./ft. x 1.488 = kg/meter
Choosing Between Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe for Optimal Pipeline Performance
When designing pipeline systems for oil and gas transportation, understanding the distinct characteristics and applications of welded versus seamless steel pipe is crucial for ensuring optimal system performance, cost-effectiveness, and operational reliability. The Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe Schedule Weight Chart provides essential reference data that helps engineers and procurement specialists make informed decisions based on specific project requirements, pressure ratings, and budget considerations. At FlowTech Energy, we maintain an extensive inventory of both welded and seamless steel pipe across all standard schedules and weights, allowing operators to select the ideal pipe type for their specific application needs.
Our experienced technical team can help you navigate the critical decision between welded and seamless pipe, ensuring you choose the right solution based on your specific operational parameters, pressure requirements, and budget constraints. We understand that seamless pipe offers superior pressure resistance and uniform strength for critical applications, while welded pipe provides cost advantages and consistent wall thickness for standard service conditions. Contact us today at 1-877-645-6693 to discuss how our comprehensive inventory of quality welded and seamless steel pipe can provide the perfect balance of performance characteristics and value for your next pipeline project. Whether you’re working with high-pressure applications demanding seamless pipe integrity or standard service conditions where welded pipe offers optimal economics, our selection of API-compliant steel pipe ensures you’ll find the exact specifications needed to maximize both operational reliability and cost-effectiveness throughout your pipeline system’s lifecycle.
Go here if you are looking for the Line Pipe Schedule 140 Dimension, Weight, and Thickness Chart


