Casing Dimensions and Bit Clearance Chart
Oil production was a complicated process in the past. Today, the process has become cost-efficient and has been simplified by modern tools and technologies. It now consists of three phases–drilling, casing, and tubing.
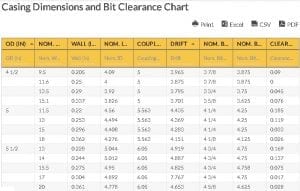
In casing, one of the tools used is the line pipe which transports oil, gas, and other natural resources extracted from the ground. The line pipe would only be useful in the completion of the petroleum exploration and production goal if the correct casing dimensions are selected. Thus, a bit clearance chart is needed alongside the casing dimensions to determine how to select the right size and meet the targeted oilfield production.
Line Pipe Designs
Before presenting the casing dimensions and bit clearance chart, one needs to become familiar with the function of the line pipe itself. The line pipe is what protects the soil from being contaminated by the drilling mud and other fluids which may be utilized during the whole extraction process.
This is what makes the selection of the casing size and bit size important, as these dimensions determine if a wellbore becomes successful or not. Ultimately, the incorrect matching of sizes can lead to drilling holes that may be problematic. Thus, the design of the line pipe is integral to its use in the industry.
Line pipe is manufactured under metallurgical specifications and regulations set by the American Petroleum Institute (API). As a standard, it is recognized worldwide as seen in the API casing dimensions and bit clearance chart below:
Casing Dimensions and Bit Clearance Chart
| OD (in) | N. Wgt PPF (lb) | Wall (in) | N.ID | C.OD | Drift | Nom. Bit Size(in) | Nom. Bit Size(Deci.) | Clear. From Drift Dia(in) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | N. Wgt PPF (lb) | Wall (in) | N.ID | C.OD | Drift | Nom. Bit Size(in) | Nom. Bit Size(Deci.) | Clear. From Drift Dia(in) |
| 1 | 4 1/2 | 9.5 | 0.205 | 4.09 | 5 | 3.965 | 3 7/8 | 3.875 | 0.09 |
| 2 | 11.6 | 0.25 | 4 | 5 | 3.875 | 3 7/8 | 3.875 | 0 | |
| 3 | 13.5 | 0.29 | 3.92 | 5 | 3.795 | 3 3/4 | 3.75 | 0.045 | |
| 4 | 15.1 | 0.337 | 3.826 | 5 | 3.701 | 3 5/8 | 3.625 | 0.076 | |
| 5 | 5 | 11.5 | 0.22 | 4.56 | 5.563 | 4.435 | 4 1/4 | 4.25 | 0.185 |
| 6 | 13 | 0.253 | 4.494 | 5.563 | 4.369 | 4 1/4 | 4.25 | 0.119 | |
| 7 | 15 | 0.296 | 4.408 | 5.563 | 4.283 | 4 1/4 | 4.25 | 0.033 | |
| 8 | 18 | 0.362 | 4.276 | 5.563 | 4.151 | 4 1/8 | 4.125 | 0.026 | |
| 9 | 5 1/2 | 13 | 0.228 | 5.044 | 6.05 | 4.919 | 4 3/4 | 4.75 | 0.169 |
| 10 | 14 | 0.244 | 5.012 | 6.05 | 4.887 | 4 3/4 | 4.75 | 0.137 | |
| 11 | 15.5 | 0.275 | 4.95 | 6.05 | 4.825 | 4 3/4 | 4.758 | 0.075 | |
| 12 | 17 | 0.304 | 4.892 | 6.05 | 7.767 | 4 3/4 | 4.75 | 0.017 | |
| 13 | 20 | 0.361 | 4.778 | 6.05 | 4.653 | 4 5/8 | 4.625 | 0.028 | |
| 14 | 23 | 0.415 | 4.67 | 6.05 | 4.545 | 4 1/2 | 4.5 | 0.045 | |
| 15 | 6 | 15 | 0.238 | 5.524 | 6.625 | 5.399 | 5 3/8 | 5.375 | 0.024 |
| 16 | 18 | 0.288 | 5.424 | 6.625 | 5.299 | 5 1/8 | 5.125 | 0.174 | |
| 17 | 20 | 0.324 | 5.352 | 6.625 | 5.227 | 5 1/8 | 5.125 | 0.102 | |
| 18 | 23 | 0.38 | 5.24 | 6.625 | 5.115 | 4 7/8 | 4.875 | 0.24 | |
| 19 | 26 | 0.434 | 5.132 | 6.625 | 5.007 | 4 7/8 | 4.875 | 0.132 | |
| 20 | 6 5/8 | 17 | 0.245 | 6.135 | 7.39 | 6.01 | 6 | 6 | 0.01 |
| 21 | 20 | 0.288 | 6.049 | 7.39 | 5.924 | 5 7/8 | 5.875 | 0.049 | |
| 22 | 24 | 0.352 | 5.921 | 7.39 | 5.796 | 5 3/4 | 5.75 | 0.046 | |
| 23 | 28 | 0.417 | 5.791 | 7.39 | 5.666 | 5 5/8 | 5.625 | 0.041 | |
| 24 | 32 | 0.475 | 5.675 | 7.39 | 5.55 | 5 3/8 | 5.375 | 0.175 | |
| 25 | 7 | 17 | 0.231 | 6.538 | 7.656 | 6.413 | 6 3/8 | 6.375 | 0.038 |
| 26 | 20 | 0.272 | 6.456 | 7.656 | 6.331 | 6 1/4 | 6.25 | 0.081 | |
| 27 | 23 | 0.317 | 6.366 | 7.656 | 6.241 | 6 1/8 | 6.125 | 0.116 | |
| 28 | 26 | 0.362 | 6.276 | 7.656 | 6.151 | 6 1/8 | 6.125 | 0.026 | |
| 29 | 29 | 0.408 | 5.184 | 7.656 | 6.059 | 6 | 6 | 0.059 | |
| 30 | 32 | 0.453 | 6.094 | 7.656 | 5.969 | 5 7/8 | 5.875 | 0.094 | |
| 31 | 35 | 0.498 | 6.004 | 7.656 | 5.879 | 5 7/8 | 5.875 | 0.004 | |
| 32 | 38 | 0.54 | 5.92 | 7.656 | 5.795 | 5 3/4 | 5.75 | 0.045 | |
| 33 | 7 5/8 | 20 | 0.25 | 4.125 | 8.5 | 7 | 6 3/4 | 6.75 | 0.25 |
| 34 | 24 | 0.3 | 7.025 | 8.5 | 6.9 | 5 3/4 | 6.75 | 0.15 | |
| 35 | 26.4 | 0.328 | 6.969 | 8.5 | 6.844 | 6 3/4 | 6.785 | 0.094 | |
| 36 | 29.7 | 0.375 | 6.875 | 8.5 | 6.75 | 6 3/4 | 6.75 | 0 | |
| 37 | 33.7 | 0.43 | 6.765 | 8.5 | 6.64 | 6 5/8 | 6.625 | 0.015 | |
| 38 | 39 | 0.5 | 6.625 | 8.5 | 6.5 | 6 3/8 | 6.375 | 0.125 | |
| 39 | 8 5/8 | 24 | 0.264 | 8.097 | 9.625 | 7.972 | 7 7/8 | 7.875 | 0.097 |
| 40 | 28 | 0.304 | 8.017 | 9.625 | 7.892 | 7 7/8 | 7.875 | 0.017 | |
| 41 | 32 | 0.352 | 7.921 | 9.625 | 7.796 | 7 3/4 | 7.75 | 0.046 | |
| 42 | 36 | 0.4 | 7.825 | 9.625 | 7.7 | 7 5/8 | 7.625 | 0.075 | |
| 43 | 40 | 0.45 | 7.725 | 9.625 | 7.6 | 7 3/8 | 7.375 | 0.225 | |
| 44 | 44 | 0.5 | 7.625 | 9.625 | 7.5 | 7 3/8 | 7.375 | 0.125 | |
| 45 | 49 | 0.557 | 7.511 | 9.625 | 7.386 | 7 3/8 | 7.375 | 0.011 | |
| 46 | 9 5/8 | 29.3 | 0.281 | 9.063 | 10.635 | 8.907 | 8 3/4 | 8.75 | 0.157 |
| 47 | 32.3 | 0.312 | 9.001 | 10.625 | 8.845 | 8 3/4 | 8.75 | 0.095 | |
| 48 | 36 | 0.352 | 8.921 | 10.625 | 8.765 | 8 3/4 | 8.75 | 0.015 | |
| 49 | 40 | 0.395 | 8.835 | 10.625 | 8.679 | 8 5/8 | 8.625 | 0.054 | |
| 50 | 43.5 | 0.435 | 8.755 | 10.625 | 8.599 | 8 1/2 | 8.5 | 0.099 |
Casing Dimensions and Bit Clearance Chart
| OD (in) | N. Wgt PPF (lb) | Wall (in) | N.ID | C.OD | Drift | Nom. Bit Size(in) | Nom. Bit Size(Deci.) | Clear. From Drift Dia(in) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | N. Wgt PPF (lb) | Wall (in) | N.ID | C.OD | Drift | Nom. Bit Size(in) | Nom. Bit Size(Deci.) | Clear. From Drift Dia(in) |
| 1 | 4 1/2 | 9.5 | 0.205 | 4.09 | 5 | 3.965 | 3 7/8 | 3.875 | 0.09 |
| 2 | 11.6 | 0.25 | 4 | 5 | 3.875 | 3 7/8 | 3.875 | 0 | |
| 3 | 13.5 | 0.29 | 3.92 | 5 | 3.795 | 3 3/4 | 3.75 | 0.045 | |
| 4 | 15.1 | 0.337 | 3.826 | 5 | 3.701 | 3 5/8 | 3.625 | 0.076 | |
| 5 | 5 | 11.5 | 0.22 | 4.56 | 5.563 | 4.435 | 4 1/4 | 4.25 | 0.185 |
| 6 | 13 | 0.253 | 4.494 | 5.563 | 4.369 | 4 1/4 | 4.25 | 0.119 | |
| 7 | 15 | 0.296 | 4.408 | 5.563 | 4.283 | 4 1/4 | 4.25 | 0.033 | |
| 8 | 18 | 0.362 | 4.276 | 5.563 | 4.151 | 4 1/8 | 4.125 | 0.026 | |
| 9 | 5 1/2 | 13 | 0.228 | 5.044 | 6.05 | 4.919 | 4 3/4 | 4.75 | 0.169 |
| 10 | 14 | 0.244 | 5.012 | 6.05 | 4.887 | 4 3/4 | 4.75 | 0.137 | |
| 11 | 15.5 | 0.275 | 4.95 | 6.05 | 4.825 | 4 3/4 | 4.758 | 0.075 | |
| 12 | 17 | 0.304 | 4.892 | 6.05 | 7.767 | 4 3/4 | 4.75 | 0.017 | |
| 13 | 20 | 0.361 | 4.778 | 6.05 | 4.653 | 4 5/8 | 4.625 | 0.028 | |
| 14 | 23 | 0.415 | 4.67 | 6.05 | 4.545 | 4 1/2 | 4.5 | 0.045 | |
| 15 | 6 | 15 | 0.238 | 5.524 | 6.625 | 5.399 | 5 3/8 | 5.375 | 0.024 |
| 16 | 18 | 0.288 | 5.424 | 6.625 | 5.299 | 5 1/8 | 5.125 | 0.174 | |
| 17 | 20 | 0.324 | 5.352 | 6.625 | 5.227 | 5 1/8 | 5.125 | 0.102 | |
| 18 | 23 | 0.38 | 5.24 | 6.625 | 5.115 | 4 7/8 | 4.875 | 0.24 | |
| 19 | 26 | 0.434 | 5.132 | 6.625 | 5.007 | 4 7/8 | 4.875 | 0.132 | |
| 20 | 6 5/8 | 17 | 0.245 | 6.135 | 7.39 | 6.01 | 6 | 6 | 0.01 |
| 21 | 20 | 0.288 | 6.049 | 7.39 | 5.924 | 5 7/8 | 5.875 | 0.049 | |
| 22 | 24 | 0.352 | 5.921 | 7.39 | 5.796 | 5 3/4 | 5.75 | 0.046 | |
| 23 | 28 | 0.417 | 5.791 | 7.39 | 5.666 | 5 5/8 | 5.625 | 0.041 | |
| 24 | 32 | 0.475 | 5.675 | 7.39 | 5.55 | 5 3/8 | 5.375 | 0.175 | |
| 25 | 7 | 17 | 0.231 | 6.538 | 7.656 | 6.413 | 6 3/8 | 6.375 | 0.038 |
| 26 | 20 | 0.272 | 6.456 | 7.656 | 6.331 | 6 1/4 | 6.25 | 0.081 | |
| 27 | 23 | 0.317 | 6.366 | 7.656 | 6.241 | 6 1/8 | 6.125 | 0.116 | |
| 28 | 26 | 0.362 | 6.276 | 7.656 | 6.151 | 6 1/8 | 6.125 | 0.026 | |
| 29 | 29 | 0.408 | 5.184 | 7.656 | 6.059 | 6 | 6 | 0.059 | |
| 30 | 32 | 0.453 | 6.094 | 7.656 | 5.969 | 5 7/8 | 5.875 | 0.094 | |
| 31 | 35 | 0.498 | 6.004 | 7.656 | 5.879 | 5 7/8 | 5.875 | 0.004 | |
| 32 | 38 | 0.54 | 5.92 | 7.656 | 5.795 | 5 3/4 | 5.75 | 0.045 | |
| 33 | 7 5/8 | 20 | 0.25 | 4.125 | 8.5 | 7 | 6 3/4 | 6.75 | 0.25 |
| 34 | 24 | 0.3 | 7.025 | 8.5 | 6.9 | 5 3/4 | 6.75 | 0.15 | |
| 35 | 26.4 | 0.328 | 6.969 | 8.5 | 6.844 | 6 3/4 | 6.785 | 0.094 | |
| 36 | 29.7 | 0.375 | 6.875 | 8.5 | 6.75 | 6 3/4 | 6.75 | 0 | |
| 37 | 33.7 | 0.43 | 6.765 | 8.5 | 6.64 | 6 5/8 | 6.625 | 0.015 | |
| 38 | 39 | 0.5 | 6.625 | 8.5 | 6.5 | 6 3/8 | 6.375 | 0.125 | |
| 39 | 8 5/8 | 24 | 0.264 | 8.097 | 9.625 | 7.972 | 7 7/8 | 7.875 | 0.097 |
| 40 | 28 | 0.304 | 8.017 | 9.625 | 7.892 | 7 7/8 | 7.875 | 0.017 | |
| 41 | 32 | 0.352 | 7.921 | 9.625 | 7.796 | 7 3/4 | 7.75 | 0.046 | |
| 42 | 36 | 0.4 | 7.825 | 9.625 | 7.7 | 7 5/8 | 7.625 | 0.075 | |
| 43 | 40 | 0.45 | 7.725 | 9.625 | 7.6 | 7 3/8 | 7.375 | 0.225 | |
| 44 | 44 | 0.5 | 7.625 | 9.625 | 7.5 | 7 3/8 | 7.375 | 0.125 | |
| 45 | 49 | 0.557 | 7.511 | 9.625 | 7.386 | 7 3/8 | 7.375 | 0.011 | |
| 46 | 9 5/8 | 29.3 | 0.281 | 9.063 | 10.635 | 8.907 | 8 3/4 | 8.75 | 0.157 |
| 47 | 32.3 | 0.312 | 9.001 | 10.625 | 8.845 | 8 3/4 | 8.75 | 0.095 | |
| 48 | 36 | 0.352 | 8.921 | 10.625 | 8.765 | 8 3/4 | 8.75 | 0.015 | |
| 49 | 40 | 0.395 | 8.835 | 10.625 | 8.679 | 8 5/8 | 8.625 | 0.054 | |
| 50 | 43.5 | 0.435 | 8.755 | 10.625 | 8.599 | 8 1/2 | 8.5 | 0.099 |
Casing Dimensions and Bit Clearance Chart Components
In the chart, the dynamics of a well’s performance (in connection to the casing) are tabulated. On the leftmost part of the table, the outer diameter (OD) is used to specify a casing. Different sizes cater to different hole dimensions. Next is the nominal weight which is the average linear weight of the tubing that includes the connection type or the kind of thread that is utilized to connect the joints of the casing. What makes this figure important is that it also determines the thickness of the tubing wall that specifies the nominal inner diameter (ID).
The kind of thread mentioned earlier is called collar or coupling that is slightly larger in diameter than the joints. It is used to connect the two joint ends. Lastly, the drift diameter, in connection to the bit size used in drilling, is what controls the bit selection for the open hole below the casing. Being the guaranteed inner diameter, it is typically smaller than the nominal inner diameter.
All these make up the Casing Dimensions and Bit Clearance Chart which contains some of the basic factors that are important in the oil production process.
Casing Dimensions and Bit Clearance Chart Abbreviations:
- OD – Outside Diameter
- ID – Inside Diameter
- Drift Dia. – Drift Diameter
- N.Wgt PPF (lb) – Weight Per Foot Nominal Pound
- N.ID – Nominal Inside Diameter
- C.OD – Coupling Outside Diameter
- Nom. Bit Size(in) – Nominal Bit Size (Inches)
- Nom. Bit Size(Deci.) – Nominal Bit Size (Decimal)
- Clear. From Drift Dia(in) – Clearance From Drift Diameter(Inches)
Go here if you are looking for the ERW Casing Grade and Connection Type Chart.


