Tubing Torque for Long-Thread Chart
 Thread, Casing and Tubing: Uses for Petroleum Engineering
Thread, Casing and Tubing: Uses for Petroleum Engineering
The thread in tubing pertains to the helical ridge formed inside or outside the tube’s end. A thread constitutes a crest (ridge), a root (the space between the ridge), and the helix angle that is either upward or sloped. Threads are used to connect two pipes where the other one has a large inner diameter or casing than the other.
In petroleum engineering terms, the casing is the hollow steel pipe that surrounds or lines the drilled hole. A casing is used to protect the underground aquifers and groundwater from oil and gas contamination; control well pressures during production, workover operations and drilling; and maintain borehole stability. A tubing is smaller than the casing; the threshold that differentiates the two is an outer diameter of 114.3 mm or 4 ½ inches.
Long Thread in Joint Connections
The American Petroleum Institute (API) recognizes the basic types of joint connections:
- Asymmetrical and Trapezoidal thread buttress coupling
- Coupling without the extreme-line casing with trapezoidal thread
- Rounded thread (long and short) coupling
The long thread casing (LTC) has 8 threads per inch compared to short thread casing (STC).
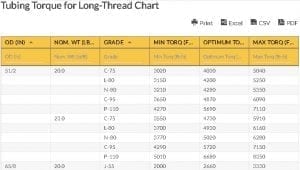
Tubing Torque for Long-Thread Chart
The Long-Thread Chart of Tubing Torque specifies the Outer Diameter (OD) in inches, the weight measured in lb and ft, and the grades of casing pipes that differ in hardness, yield, and tensile strength.
The Chart for the Long Thread and Tubing Torque features three outer diameter sizes in inches that differ in nominal weight measured in lb and ft. This nominal weight covers casing grades (C-75, L-80, N-80, C-95, P-110) that feature different torque measurements categorized into minimum, optimum, and maximum. A torque is a twisting force that rotates an object or fluid.
The Long-Thread Chart of Tubing Torque also shows the various grades that differ in use, yield strength, tensile strength, and hardness.
Tubing Torque for Long-Thread Chart
| OD (in) | Nom. Wt (lb/ft) | Grade | Min Torq (ft-lb) | Opti. Torq (ft-lb) | Max Torq (ft-lb) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | Nom. Wt (lb/ft) | Grade | Min Torq (ft-lb) | Opti. Torq (ft-lb) | Max Torq (ft-lb) |
| 1 | 51/2 | 20.0 | C-75 | 3020 | 4030 | 5040 |
| 2 | L-80 | 3150 | 4200 | 5250 | ||
| 3 | N-80 | 3210 | 4280 | 5350 | ||
| 4 | C-95 | 3650 | 4870 | 6090 | ||
| 5 | P-110 | 4270 | 5690 | 7110 | ||
| 6 | 23.0 | C-75 | 3550 | 4730 | 5910 | |
| 7 | L-80 | 3700 | 4930 | 6160 | ||
| 8 | N-80 | 3770 | 5020 | 6280 | ||
| 9 | C-95 | 4290 | 5720 | 7150 | ||
| 10 | P-110 | 5010 | 6680 | 8350 | ||
| 11 | 65/8 | 20.0 | J-55 | 2000 | 2660 | 3330 |
| 12 | K-55 | 2180 | 2900 | 3630 | ||
| 13 | 24.0 | J-55 | 2550 | 3400 | 4250 | |
| 14 | K-55 | 2790 | 3720 | 4650 | ||
| 15 | C-75 | 3400 | 4530 | 5660 | ||
| 16 | L-80 | 3550 | 4730 | 5910 | ||
| 17 | N-80 | 3610 | 4810 | 6010 | ||
| 18 | C-95 | 4120 | 5490 | 6860 | ||
| 19 | P-110 | 4810 | 6410 | 8010 | ||
| 20 | 28.0 | C-75 | 4140 | 5520 | 6900 | |
| 21 | L-80 | 4320 | 5760 | 7200 | ||
| 22 | N-80 | 4400 | 5860 | 7330 | ||
| 23 | C-95 | 5020 | 6690 | 8360 | ||
| 24 | P-110 | 5860 | 7810 | 9760 | ||
| 25 | 32.0 | C-75 | 4790 | 6380 | 7980 | |
| 26 | L-80 | 5000 | 6660 | 8330 | ||
| 27 | N-80 | 5080 | 6770 | 6460 | ||
| 28 | C-95 | 5810 | 7740 | 9680 | ||
| 29 | P-110 | 6780 | 9040 | 11300 | ||
| 30 | 7 | 23.0 | J-55 | 2350 | 3130 | 3910 |
| 31 | K-55 | 2560 | 3410 | 4260 | ||
| 32 | C-75 | 3120 | 4160 | 5200 | ||
| 33 | L-80 | 3260 | 4350 | 5440 | ||
| 34 | N-80 | 3320 | 4420 | 5530 | ||
| 35 | C-95 | 3790 | 5050 | 6310 | ||
| 36 | 26.0 | J-55 | 2750 | 3670 | 4590 | |
| 37 | K-55 | 3010 | 4010 | 5010 | ||
| 38 | C-75 | 3670 | 4890 | 6110 | ||
| 39 | L-80 | 3830 | 5110 | 6390 | ||
| 40 | N-80 | 3890 | 5190 | 6490 | ||
| 41 | C-95 | 4450 | 5930 | 7410 | ||
| 42 | P-110 | 5200 | 6930 | 6660 | ||
| 43 | 29.0 | C-75 | 4220 | 5620 | 7030 | |
| 44 | L-80 | 4400 | 5870 | 7340 | ||
| 45 | N-80 | 4480 | 5970 | 7460 | ||
| 46 | C-95 | 5120 | 6830 | 8540 | ||
| 47 | P-110 | 5980 | 7970 | 9960 | ||
| 48 | 32.0 | C-75 | 4750 | 6330 | 7910 | |
| 49 | L-80 | 4960 | 6610 | 8260 | ||
| 50 | N-80 | 5040 | 6720 | 8400 |
Tubing Torque for Long-Thread Chart
| OD (in) | Nom. Wt (lb/ft) | Grade | Min Torq (ft-lb) | Opti. Torq (ft-lb) | Max Torq (ft-lb) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | OD (in) | Nom. Wt (lb/ft) | Grade | Min Torq (ft-lb) | Opti. Torq (ft-lb) | Max Torq (ft-lb) |
| 1 | 51/2 | 20.0 | C-75 | 3020 | 4030 | 5040 |
| 2 | L-80 | 3150 | 4200 | 5250 | ||
| 3 | N-80 | 3210 | 4280 | 5350 | ||
| 4 | C-95 | 3650 | 4870 | 6090 | ||
| 5 | P-110 | 4270 | 5690 | 7110 | ||
| 6 | 23.0 | C-75 | 3550 | 4730 | 5910 | |
| 7 | L-80 | 3700 | 4930 | 6160 | ||
| 8 | N-80 | 3770 | 5020 | 6280 | ||
| 9 | C-95 | 4290 | 5720 | 7150 | ||
| 10 | P-110 | 5010 | 6680 | 8350 | ||
| 11 | 65/8 | 20.0 | J-55 | 2000 | 2660 | 3330 |
| 12 | K-55 | 2180 | 2900 | 3630 | ||
| 13 | 24.0 | J-55 | 2550 | 3400 | 4250 | |
| 14 | K-55 | 2790 | 3720 | 4650 | ||
| 15 | C-75 | 3400 | 4530 | 5660 | ||
| 16 | L-80 | 3550 | 4730 | 5910 | ||
| 17 | N-80 | 3610 | 4810 | 6010 | ||
| 18 | C-95 | 4120 | 5490 | 6860 | ||
| 19 | P-110 | 4810 | 6410 | 8010 | ||
| 20 | 28.0 | C-75 | 4140 | 5520 | 6900 | |
| 21 | L-80 | 4320 | 5760 | 7200 | ||
| 22 | N-80 | 4400 | 5860 | 7330 | ||
| 23 | C-95 | 5020 | 6690 | 8360 | ||
| 24 | P-110 | 5860 | 7810 | 9760 | ||
| 25 | 32.0 | C-75 | 4790 | 6380 | 7980 | |
| 26 | L-80 | 5000 | 6660 | 8330 | ||
| 27 | N-80 | 5080 | 6770 | 6460 | ||
| 28 | C-95 | 5810 | 7740 | 9680 | ||
| 29 | P-110 | 6780 | 9040 | 11300 | ||
| 30 | 7 | 23.0 | J-55 | 2350 | 3130 | 3910 |
| 31 | K-55 | 2560 | 3410 | 4260 | ||
| 32 | C-75 | 3120 | 4160 | 5200 | ||
| 33 | L-80 | 3260 | 4350 | 5440 | ||
| 34 | N-80 | 3320 | 4420 | 5530 | ||
| 35 | C-95 | 3790 | 5050 | 6310 | ||
| 36 | 26.0 | J-55 | 2750 | 3670 | 4590 | |
| 37 | K-55 | 3010 | 4010 | 5010 | ||
| 38 | C-75 | 3670 | 4890 | 6110 | ||
| 39 | L-80 | 3830 | 5110 | 6390 | ||
| 40 | N-80 | 3890 | 5190 | 6490 | ||
| 41 | C-95 | 4450 | 5930 | 7410 | ||
| 42 | P-110 | 5200 | 6930 | 6660 | ||
| 43 | 29.0 | C-75 | 4220 | 5620 | 7030 | |
| 44 | L-80 | 4400 | 5870 | 7340 | ||
| 45 | N-80 | 4480 | 5970 | 7460 | ||
| 46 | C-95 | 5120 | 6830 | 8540 | ||
| 47 | P-110 | 5980 | 7970 | 9960 | ||
| 48 | 32.0 | C-75 | 4750 | 6330 | 7910 | |
| 49 | L-80 | 4960 | 6610 | 8260 | ||
| 50 | N-80 | 5040 | 6720 | 8400 |
Tubing Torque for Long-Thread Chart Abbreviations:
- OD – Outside diameter
- in – inches
- lb/ft – pound per feet
- ft-lb – foot-pound
- Min Torq – Minimum Torque
- Max Torq – Maximum Torque
- Opti Torq – Optimum Torque
- Nom Wt – Nominal Weight
Common Application Casing (R95, M65, N80, J55, K55, H40)
These are commonly used in wells that do not demand stringent strength and anti-corrosion requirements. The following are the descriptions of two grades – H40 and K55.
H40
API color code: 1 black band or none
Minimum tensile strength: 414 MPa or 60 ksi or kilopound per square inch
Yield strength: 276-552 MPa (Megapascal) or 40-80 ksi or kilopound per square inch
K55
Similar to grade J55 in yield but has a minimum tensile strength 26% higher compared to J55
API color code: Two bright green bands
Minimum tensile strength: 665 MPa or 95 ksi
Yield strength: 379-552 MPa or 55-80 ksi
Corrosion-Resistant Casing (C90, L80, C110, T95)
This grade features high resistance to stress cracking in H2S (Hydrogen Sulfide) environments.
Grades L80-13Cr and L80-9Cr are suited for use in CO2 environments due to their higher chromium content.
C90
API color code: One purple band
Minimum tensile strength: 689 Megapascals or 100 kilopounds per square inch
Yield strength: 621-724 MPa or 90-105 ksi
Deep Well Casings (Q125 and P110)
These grades are suitable for deep wells with high-pressure formations but not in H2S environments because steel is vulnerable to sulfide stress cracking.
Q125 or Q125-1
API color code: One orange band
Minimum tensile strength: 931 Megapascals or 135 kilopounds per square inch
Yield strength: 862-1,034 MPa or 125-150 ksi
P110
API color code: One white band
Minimum tensile strength: 862 MPa or 125 ksi
Yield strength: 758-965 Mpa or 110-140 ksi
Pros of Long Thread Casing
Long thread (LTC) is common in casing pipe connections. LTC has advantages such as strong connection strength, better sealing properties, low price, and easy process compared to the STC that provides less coupling strength.
Effects of Torque on Drilling
In the oil and gas industry, torque can increase in extended reach and horizontal reach wells. It can limit the extended reach of well, drilling, and post-drilling activities. Buckling can increase the drag and torque, resulting in higher friction. In such a scenario, an accurate calculation is essential for the drilling operation.
Go here if you are looking for the Tubing Torque for Short-Thread Chart.


